Table of Contents
- What is Frontend Development?
- What is Backend Development?
- Key Differences Between Frontend and Backend
- Common Technologies Used
- Frontend vs Backend: Career Paths
- Can One Developer Do Both?
- How They Work Together
- Which Should You Choose?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
1. What is Frontend Development?
Frontend development focuses on the visual and interactive elements of a website or application—the parts that users interact with directly. It involves everything you see on your screen, such as the layout, fonts, colors, buttons, forms, and animations. A frontend developer’s job is to take design files from UI/UX designers and translate them into fully functional user interfaces using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
They also ensure the application is responsive, meaning it works well across different screen sizes and devices. Frontend developers need to be mindful of user experience (UX), accessibility standards, and performance optimization. They are responsible for making the web not only functional but also beautiful and user-friendly.
2. What is Backend Development?
Backend development refers to the server-side logic and database interactions that power web applications. While users don’t directly see the backend, it’s the backbone of any digital product. Backend developers are responsible for writing code that processes data, performs business logic, manages user authentication, and ensures secure communication between the server and client.
They use languages like Python, Java, PHP, Ruby, and JavaScript (Node.js), and work with databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. Backend developers also create APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that frontend applications can use to request and send data. Ultimately, the backend handles everything that happens behind the curtain to make sure the application runs efficiently and securely.
3. Key Differences Between Frontend and Backend
Frontend and backend development differ in several fundamental ways. The most obvious distinction lies in what they handle—frontend is about what users see and interact with, while backend is about the data, servers, and application logic that users don’t see. Frontend developers primarily work with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, along with frameworks like React or Angular.
On the other hand, backend developers use languages such as Python, PHP, or Node.js, and deal with databases, authentication, and server management. While frontend development emphasizes design, responsiveness, and interactivity, backend development focuses on performance, scalability, and data processing. These two roles require different skill sets but must collaborate closely to deliver a cohesive product.
| Feature | Frontend | Backend |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | User Interface and Experience | Server, Database, and Logic |
| Languages | HTML, CSS, JavaScript | Python, Ruby, PHP, Node.js |
| Tools | React, Angular, Vue.js | Express.js, Django, Laravel |
| Interactions | Direct user interactions | Indirect (server-side operations) |
| Runs on | Browser | Server |
| Data Handling | Fetch/display data | Create/process/manage data |
4. Common Technologies Used
Both frontend and backend development rely on specific sets of tools, frameworks, and technologies that help developers build modern, efficient applications. In frontend development, HTML provides the structure, CSS styles the content, and JavaScript adds interactivity. Frameworks and libraries such as React, Vue.js, and Angular are commonly used to build dynamic single-page applications.
For backend development, popular languages include Python, JavaScript (Node.js), Java, PHP, and Ruby. Frameworks like Django, Flask, Laravel, and Express.js help developers build scalable server-side applications. Additionally, backend developers work with databases such as MongoDB, MySQL, and PostgreSQL, and often utilize tools like Docker, Git, AWS, and CI/CD pipelines to streamline development and deployment processes.
5. Frontend vs Backend: Career Paths
The choice between frontend and backend development as a career path largely depends on your interests and strengths. Frontend development is ideal for individuals who enjoy design, creativity, and working closely with the user interface. It’s well-suited for those with an eye for detail and a passion for creating intuitive user experiences.
Backend development is more analytical, logical, and data-driven. It’s great for people who enjoy problem-solving, working with databases, and optimizing application performance. Both roles are in high demand and offer lucrative career opportunities. Many developers also choose to become full-stack developers to broaden their skill set and work on both sides of the development process.
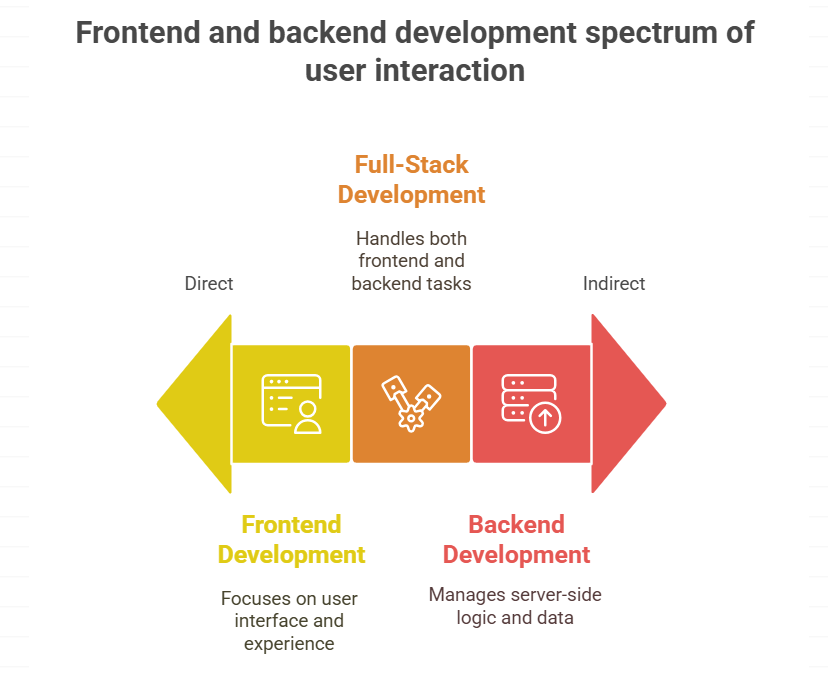
6. Can One Developer Do Both?
Yes, it’s entirely possible for one developer to handle both frontend and backend tasks. Such professionals are known as full-stack developers. They possess a well-rounded understanding of how the entire application works, from the user interface to the server logic and database. Full-stack developers are especially valuable in startups and smaller teams where versatility is key.
Common technology stacks include MERN (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js) and MEAN (MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js), among others. Being a full-stack developer requires continual learning and the ability to adapt to various tools and frameworks. While challenging, it offers the flexibility to work on end-to-end solutions and gain a broader perspective of software development.
7. How They Work Together
Frontend and backend development are two sides of the same coin. They must work in harmony to deliver a seamless and functional user experience. For example, when a user fills out a registration form on a website (frontend), the data is sent to the server (backend), which processes and stores the information in a database.
The backend then sends a response, such as a confirmation message, back to the frontend to display to the user. Effective communication between frontend and backend developers is essential for creating robust and efficient applications. This collaboration ensures that the user interface is well-integrated with the data and logic that drive it.
8. Which Should You Choose?
Choosing between frontend and backend development depends on your interests, goals, and learning style. If you enjoy visual design, interactivity, and user experience, then frontend development may be a better fit for you. It allows you to bring ideas to life in a way that directly engages users.
On the other hand, if you prefer logic, data structures, and behind-the-scenes functionality, backend development might be more appealing. Consider experimenting with both through small projects or online courses to see which resonates more with your skills and passions. Ultimately, the tech industry offers room for both specialists and generalists, so there’s no wrong choice—just the one that suits you best.
9. Conclusion
Frontend and backend development are both essential to building modern web applications. While the frontend handles everything users see and interact with, the backend takes care of data processing, logic, and server operations. Each discipline has its own set of challenges, tools, and required skill sets.
They complement each other and must work together seamlessly for an application to succeed. Whether you’re looking to build a career in tech or trying to understand the development process for your business, knowing the difference between frontend and backend is key. As technology evolves, so do these roles, offering endless opportunities for growth and innovation.
FAQs
Q1: Is frontend development easier than backend?
A: Not necessarily. Frontend requires creativity and knowledge of design principles, while backend requires strong logical and analytical skills. Both have unique challenges.
Q2: Can I become a full-stack developer without prior experience?
A: Yes, with dedication and the right learning resources, many developers become full-stack through bootcamps, online courses, and hands-on practice.
Q3: What’s a good starting point for beginners?
A: Start with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for frontend basics, and then explore backend topics like databases, APIs, and Node.js.
Q4: Do frontend and backend developers use the same tools?
A: Some tools overlap (like Git and code editors), but most tools are specific to each domain—for example, React for frontend and Django for backend.
Q5: Which role is in higher demand—frontend or backend?
A: Both are in high demand, but backend roles often require more specialized knowledge, making them slightly more competitive in certain markets.